Types of balance sheets
It’s wise to have a buffer between your current assets and liabilities to at least cover your short-term financial obligations. The data from financial statements such as a balance sheet is essential for calculating your business’ liquidities. The main purpose of the balance sheet is to show a company’s financial status. This sheet shows a company’s assets and liabilities, along with the money invested in the business. Though the balance sheet can be prepared at any time, it is mostly prepared at the end of the accounting period. A balance sheet is a financial statement that contains details of a company’s assets or liabilities at a specific point in time.
C. Equity
- It’s important to note that this balance sheet example is formatted according to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), which companies outside the United States follow.
- As you can see, the report format is a little bit easier to read and understand.
- Understanding industry benchmarks provides context and helps you evaluate a company’s financial position more effectively.
- The common stock and preferred stock accounts are calculated by multiplying the par value by the number of shares issued.
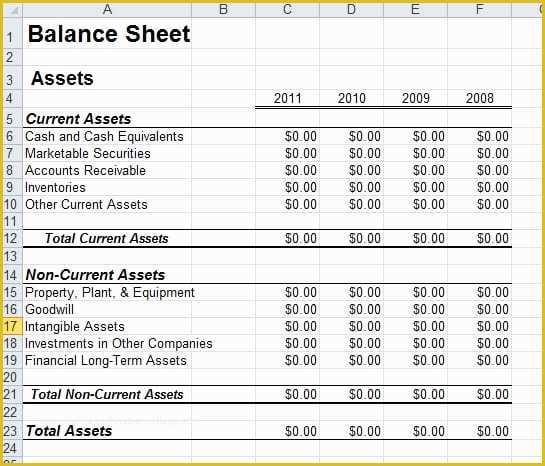
Current asset accounts include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and prepaid expenses, while long-term asset accounts include long-term investments, fixed assets, and intangible assets. A company’s balance sheet provides important information on a company’s worth, broken down into assets, liabilities, and equity. Investors can gain valuable insight from this financial statement since it shows a company’s resources and how it is funded to evaluate its financial health.
What is included in the balance sheet?
Its liabilities (specifically, the long-term debt account) will also increase by $4,000, balancing the two sides of the equation. If the company takes $8,000 from investors, its assets will increase by that amount, as will its shareholder equity. All revenues the company generates in excess of its expenses will go into the shareholder equity account.
What is the difference between the accounting balance sheet and the operating balance sheet?
Shareholder equity or Owner’s equity is the difference between a company’s assets and liabilities. Fixed assets or long-term assets are things a business owns that it plans to use for a long period of time. These intangible assets can hold significant value and contribute to a company’s overall worth.
Investment cycle, financing cycle, operating cycle and cash flow cycle
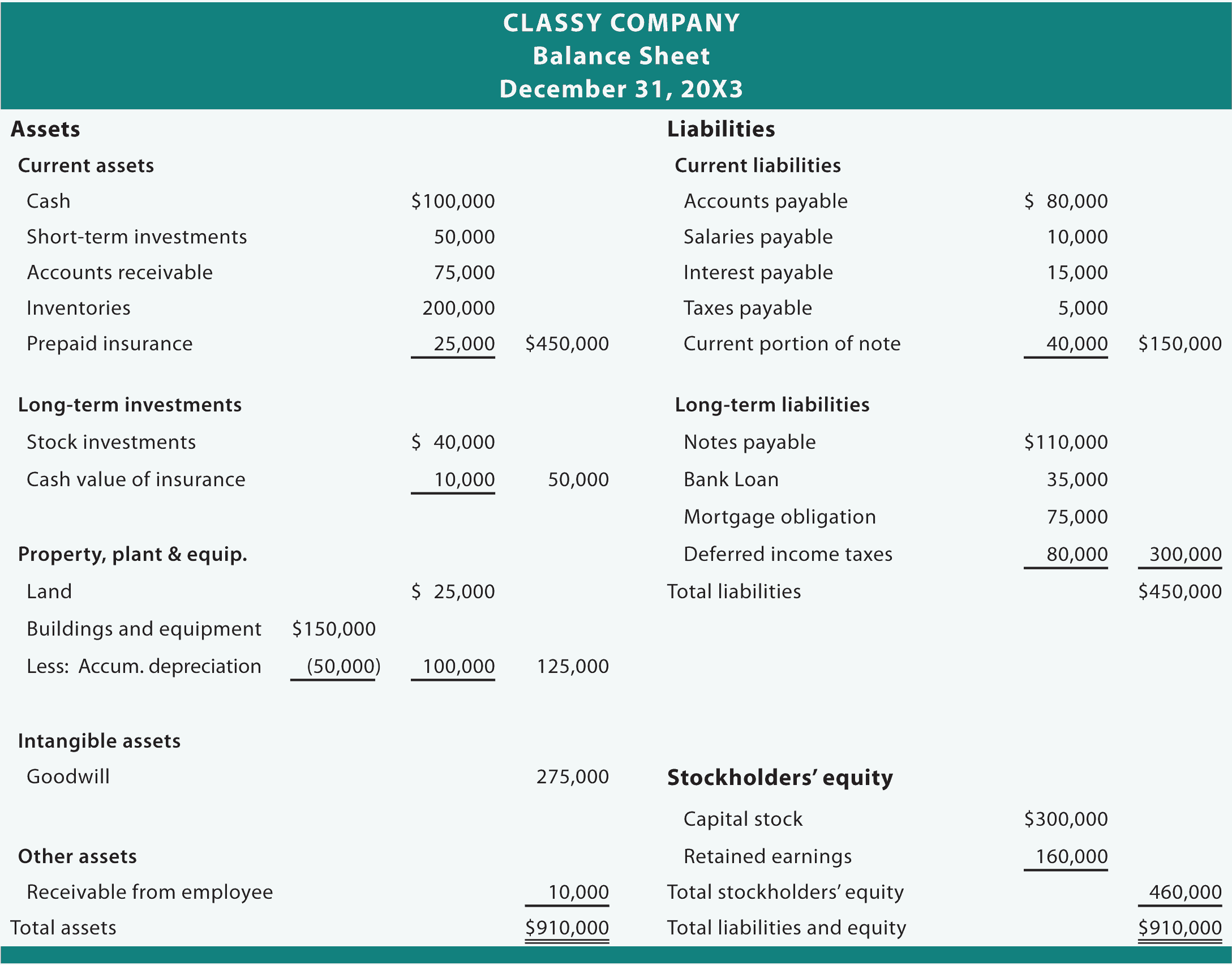
They are grouped as current liabilities and long-term liabilities in the balance sheet. Current liabilities are the obligations that are expected to be met within a period of one year by using current assets of the business or by the provision of goods or services. All liabilities that are not current liabilities are considered long-term liabilities. All assets that are not listed as current assets are grouped as non-current assets.
Using the screenshot from earlier, we’ll enter Apple’s historical balance sheet into Excel. HBS Online’s CORe and CLIMB programs require the completion of a brief application. The applications vary slightly, but all ask for some personal background best expense report templates mesh information. If you are new to HBS Online, you will be required to set up an account before starting an application for the program of your choice. All programs require the completion of a brief online enrollment form before payment.
Ensure that you meet your financial obligations and solvency goals with this easy-to-use monthly balance sheet template. Enter your assets — including cash, value of inventory, and short-term and long-term investments — as well as liabilities and owner’s equity. Completing the form will provide you with an accurate picture of your finances.
These financial statements are also key for calculating rates of return for your investors and for evaluating the capital structure of your business, both of which are essential processes. The balance sheet is prepared by either a business owner, bookkeeper or accountant. If Companies House requires it, an accountant is the best person to prepare and submit the accounts, as they will know the generally accepted accounting principles.
